-
Load template that has been cleaned in acetone and with UV/ozone into chamber
-
Cycle-purge chamber to remove water/airborne contaminants in bulk phase
-
Bake template to desorb water
-
Dose a controlled amount of water on template surface
-
Flow fluoroalkyltrichlorosilane precursor through chamber for prescribed time at prescribed temperature
-
Anneal film to enhance HCl desorption and surface/network bond formation
| This reaction sequence is
a compilation of suggestions from the literature and experience from
experiments by this group, and seems to be the best known sequence for
depositing this type of film from the gas phase. |
| The chamber was custom-milled from 316 SS,
and was designed to be only large enough to allow 1-in by 1-in SFIL
templates, thus possessing a relatively small volume. This small volume
allows for fast concentration ramp when changing from purge to water to
precursor, etc., and also for fast purge cycles, thereby maximizing
throughput. The other major components are primarily off-the-shelf, and
the schematic is shown in Figure 1. |
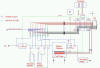 |
| Figure 1. Schematic for the SFIL surface
treatment machine. |
|
The system has a MKS 1479 mass flow controller and a MKS 640A pressure
controller, both connected to a MKS Type 146 controller which
communicates via a RS232 cable to the computer. All valves are
SS-BNVCR4-C air actuated bellows valves and are actuated by MS-SOL-2K-BN
solenoids (both Arthur Valve & Fitting); the solenoids are connected to
a National Instruments (NI) ER-8 relay pod. Temperature control is
maintained by flowing 1°C cooling fluid beneath the sample chamber, and
providing heat through a pair of cartridge heaters using on/off control;
the heaters are connected through a second ER-8 relay pod. An Omega type
K thermocouple is connected to a NI CB-50 wiring block. The ER-8 pods
and the CB-50 wiring block are connected to a NI SC-2051, which is
connected to a NI PCI-6025E data acquisition card installed in the
computer. This configuration allows completely automated process control
through a LabVIEW interface from template load to template unload. The
interface is shown in Figure 2. |
a) b)
b) |
| Figure 2. (a) Photograph of SFIL surface
treatment machine, and (b) its LabVIEW interface. |
|

 b)
b)
